深汕特别合作区赤石河一河两岸规划设计国际咨询
Planning and design of the two banks of the Chishi River in the Shenshan Special Cooperation Zone
项目背景
Project background
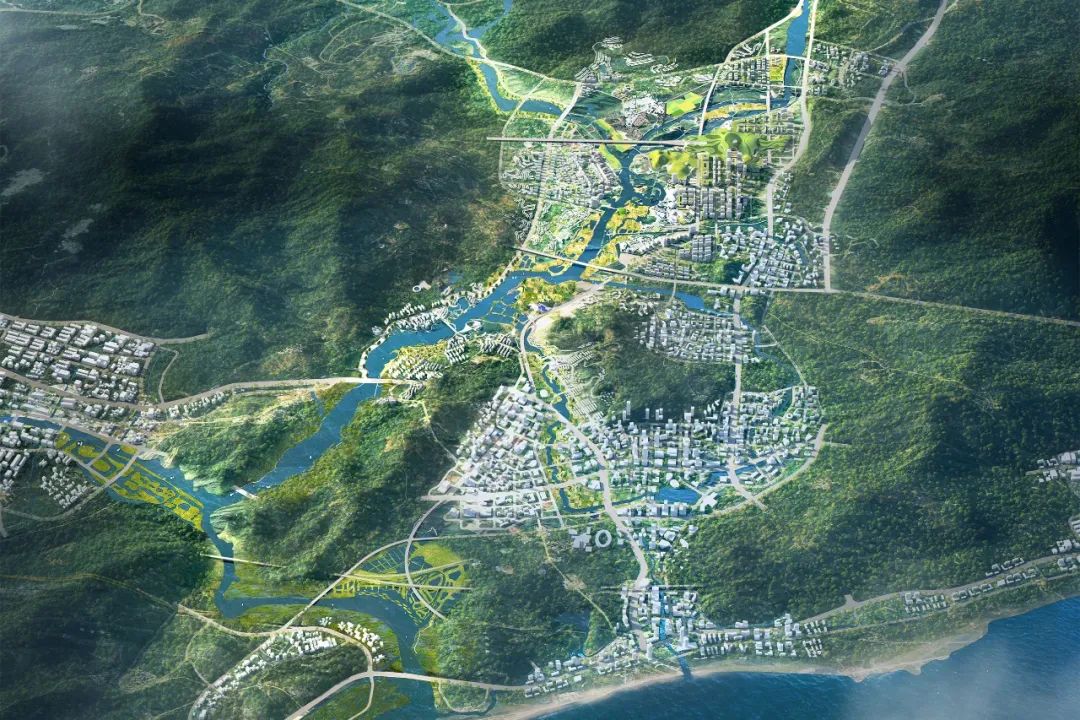
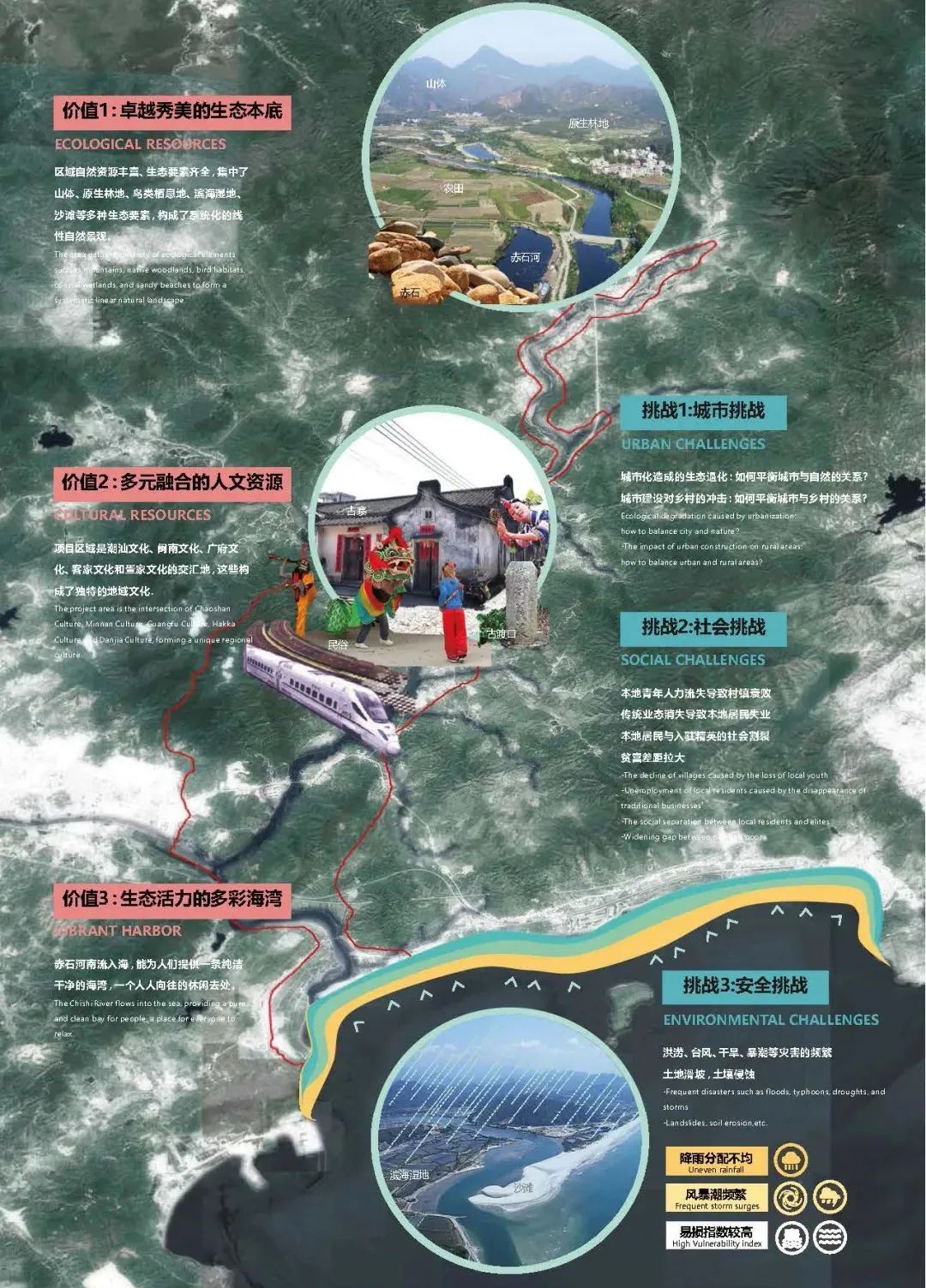
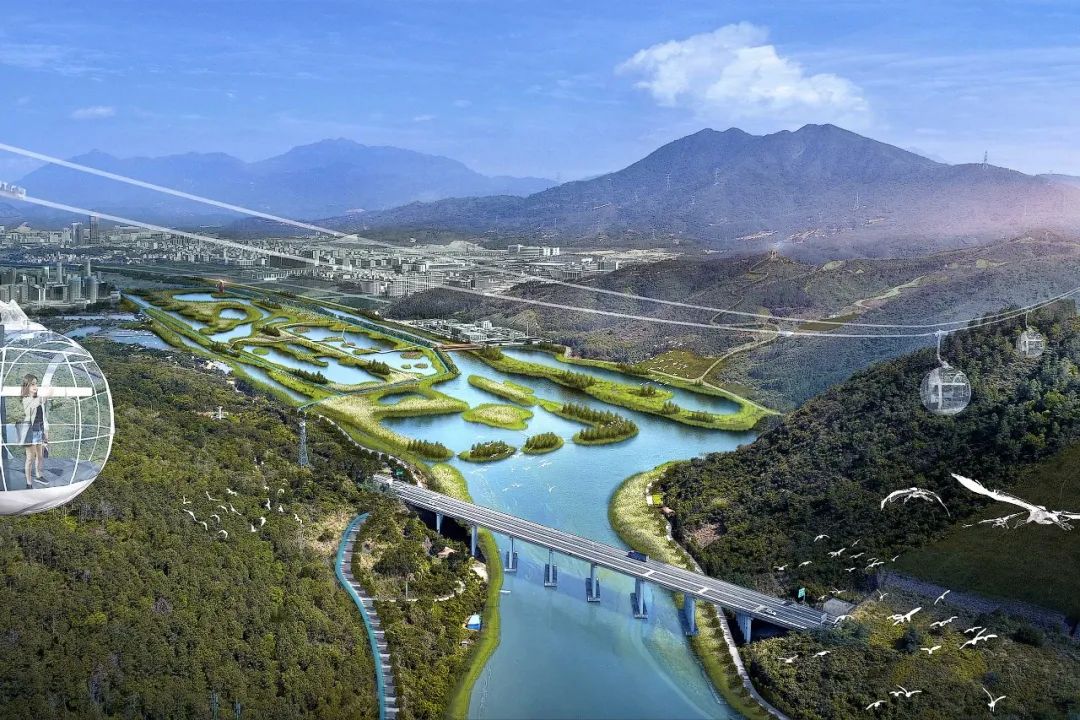
赤石河位于深圳东部——深汕特别合作区,被指定为深圳市第十一区。这条河将成为以创新为重点的新城市的中心发展走廊。它在大湾区的城市发展中发挥着关键作用。流域拥有丰富多样的宝贵生态栖息地和丰富的传统以河流为生的古老村庄的文化底蕴。
The Chishi River is located to the east of Shenzhen, in the district of Shenshan Special Cooperation Zone, designated as the 11th district of Shenzhen. Alone the river, the strip will become a new central development corridor for the city for innovation. It plays a key role in the urban development of the Great Bay Area. This river is the home to diverse flora and fauna ecological habitats and cultural heritage of traditional river-based villages.

湿地在全球均处于濒危状态。赤石的潮间带湿地尤为珍贵,1990年至2018年间,深圳已失去75%的湿地,赤石河37公里长的山川、森林、淡水、半咸水和潮间带湿地,是深圳最生态的,然而由于城市化和气候变化以及干旱和水质问题,山区、河流、涨潮、暴风雨和台风带来的洪水风险也正在增加。目前地区的人口预计将从7万增长到150万,也对当地生态、传统文化和与自然的可持续关系构成巨大压力。
Chishi’s intertidal wetlands are especially precious as Shenzhen has lost 75% of its wetlands between 1990 and 2018, and wetlands are globally endangered. With mountains, forests, freshwater, brackish and intertidal wetlands, Chishi River’s 37 kilometres are the most ecologically in Shenzhen. However, flood risks from mountain, rivers, high tides, heavy storms and typhoons are increasing due to urbanisation and climate change, in addition to droughts and water quality issues. Current population is anticipated to grow from 70,000 to 1.5 million, putting huge pressure on local ecology, traditional culture and a sustainable relationship with nature.
愿景及规划
Vision and Planning
如何解决将深圳向东延伸和城市化,是具有生态和文化价值的复杂任务,既要保护生物多样性和文化遗产,同时也需确保未来城市的气候适应能力。
赤石河流域 50 平方公里总体规划的目标是:设计该地区的气候适应能力,整合和增强生态和生物多样性,保护传统文化,同时在城市化进程中赋能当地村庄社区。
Tackles the complex task of how to extend Shenzhen eastward and urbanize the ecologically and culturally precious Chishi River Basin, preserving biodiversity and cultural heritage while ensuring climate resilience for a future city. The goals for the 50-square-kilometre master plan of Chishi River Basin are: designing for the climate resilience of the region, integrating and enhancing ecology and biodiversity, and preserving traditional culture while empowering local village communities within the process of urbanisation.

设计挑战与原则
Design Questions and Principles
未来深汕合作区将快速建设发展,至2035年(总规规划期末),从现状7万人口增长至150万人。可想而知,大规模的快速城市化将可能带来防洪安全,生态保护、居民生活生计方式改变等挑战。如何将新城市、生物多样性的山河海生态和古村落融为一体,使三者受益,设计着重研究以下三个问题:
1、如何应对水挑战,为深汕合作区打下韧性基础?
2、如何保障赤石河不可复制的生态价值?
3、如何平衡城市与乡村之间的关系,保障居民生计生活?
In the future, the Shenzhen-Shantou Cooperation Zone will develop rapidly, and by 2035 (the end of the general planning period), the population will increase from the current 70,000 to 1.5 million. It is conceivable that large-scale and rapid urbanization may bring challenges such as flood control safety, ecological protection, and changes in residents' living and livelihood styles. The design challenge is how to integrate a newcity, a biodiverse mountain-river-sea ecology and ancient villages so all three benefit. The design focuses on the following three questions:
1、How to lay the foundation for a climate resilient city?
2、How to enhance ecological value across Chishi River Basin?
3、How to preserve current village culture inside future urbanization and empower local village communities?
应用自然驱动的都市主义,并以三个设计原则为指导,这些原则体现了项目的价值和目标:
1、以水为生(气候适应力)
2、丰富的生态(生物多样性)
3、城乡和谐生活(文化遗产、活力/宜居)
Applies Nature-Driven Urbanism and is guided by three design principles that capture the values and goals of the project:
1、Living with water (climate resilience)
2、Abundant ecology (biodiversity)
3、Harmonious urban-rural living (cultural heritage, vibrancy / liveability)
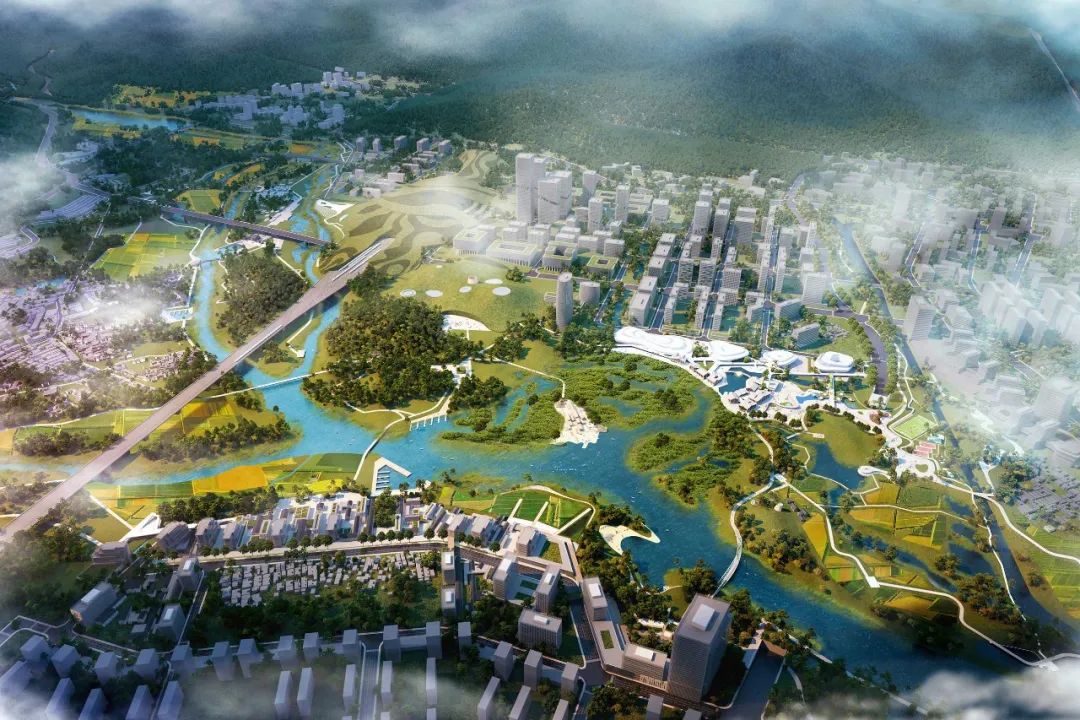
自然驱动的城市主义是一种优先考虑生态、气候适应和当地居民需求的城市规划方法。总体规划提出了一个蓝绿框架,由山地公园、山脚公园、河流公园、农业公园和城市公园组成,作为城乡居民点的基础。保护措施,即堤坝、蓄水或洪泛区,变成了丰富生物多样性的景观特征。与此同时,现有村庄通过保持其农田、池塘和森林完整而得以保护,以维持传统生计。
Nature-Driven Urbanism is an urban planning approach that prioritizes ecology, climate adaptation, and the needs of local residents. The master plan proposes a blue-green framework, which consists of mountain parks, mountain foot parks, river parks, agri parks and urban parks,as the foundation for both rural and urban settlements. Protective measures, i.e. dikes, water storage or floodplains, are turned into landscape features that enrich biodiversity. Meanwhile, existing villages are preserved by keeping their farmlands, ponds and forests intact that sustain traditional livelihoods.
设计策略
Design Strategy
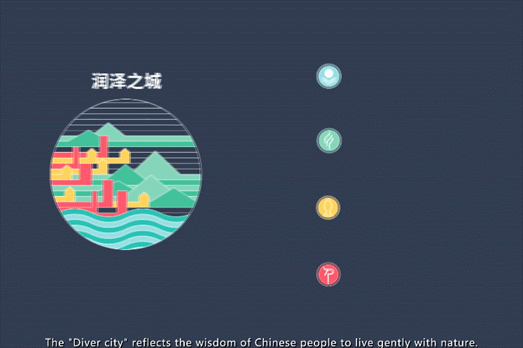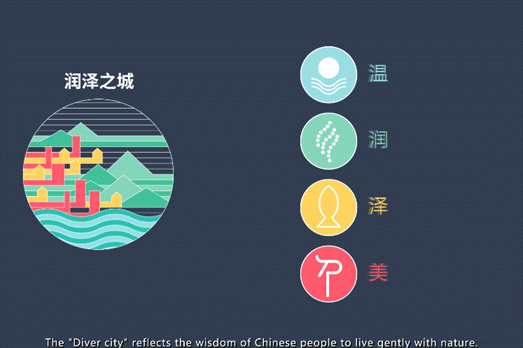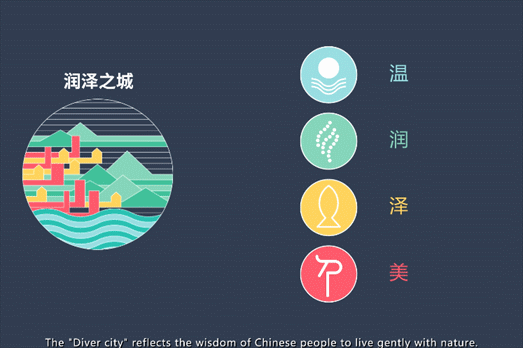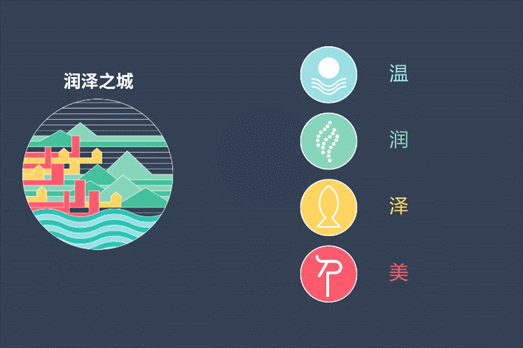
设计致力于创造生态与社会双传承的新型城市发展方案,通过对不同界面空间的系统整合,缜密平衡自然、城市、乡村三者关系,使之互相泽益彼此,“润泽之城”的理念由此而生。基于愿景,提出“温润泽美”的策略,自然滋养城市,城市善待自然,体现中国人与自然温和相处的智慧。
The design is committed to creating a new urban development plan with dual inheritance of ecology and society. Through the systematic integration of different interface spaces, the relationship between nature, city and countryside can be balanced to benefit each other. Based on the vision, the design strategy of "warm and beautiful" is proposed. Nourish the city, the city treats nature kindly, "Moisturizing City" embodies the wisdom of Chinese people to live in harmony with nature.
气候恢复力 Climate Resilience



一、从占流域面积 64.1% 的山区源头管理开始,提出了多种措施来保持水和减少径流,扩大现有山区水库蓄水能力,赤石河及其支流每年将额外蓄水96万立方米。其次,扩大天然洪泛区,保护河流生态,增加洪水容量,具有确定洪水频率的功能;
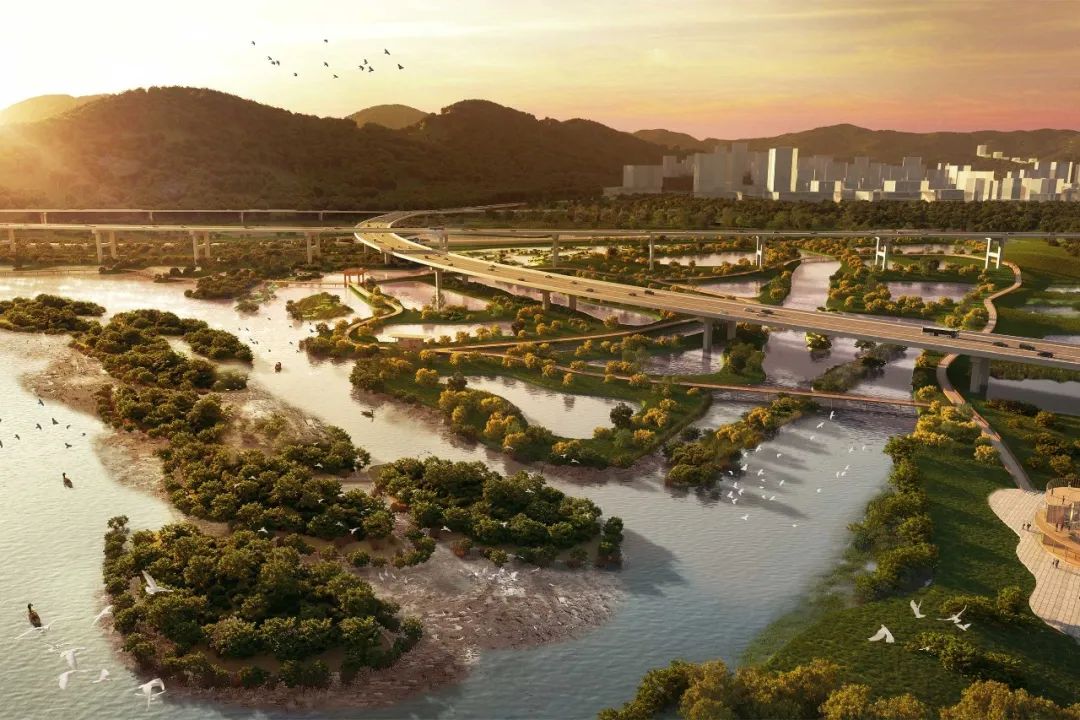
二、双堤系统为农业用地提供保护,同时创造风景小径、自行车道和观景台;
三、进一步缓解海洪压力,牡蛎岛在河口占地13万平方米,在丰富河口生态的同时降低峰值流速和波浪;
四、通过构建全市的城市蓝绿网络,实现局部雨水滞留和城市径流控制。为改善赤石河水质,在支流河道实施天然水净化措施;
五、通过智能在线系统优化整个流域的水资源管理,该系统集成了先进的建模、水质和水量监测以及洪水预警。
Starting with source management in the mountains, which comprise 64.1% of the basin area, various measures are proposed to hold water and reduce run off. The water storage capacity of existing mountain water reservoirs is enlarged. In the Chishi river and its tributaries an extra 960000m3 of water will be stored yearly. Expand the natural floodplain to protect the river ecology and increase flood capacity, with flood frequency determining functions.
Secondly, The double dike system provides protection to agricultural land while creating scenic trails, bicycle lanes, and viewing platforms.
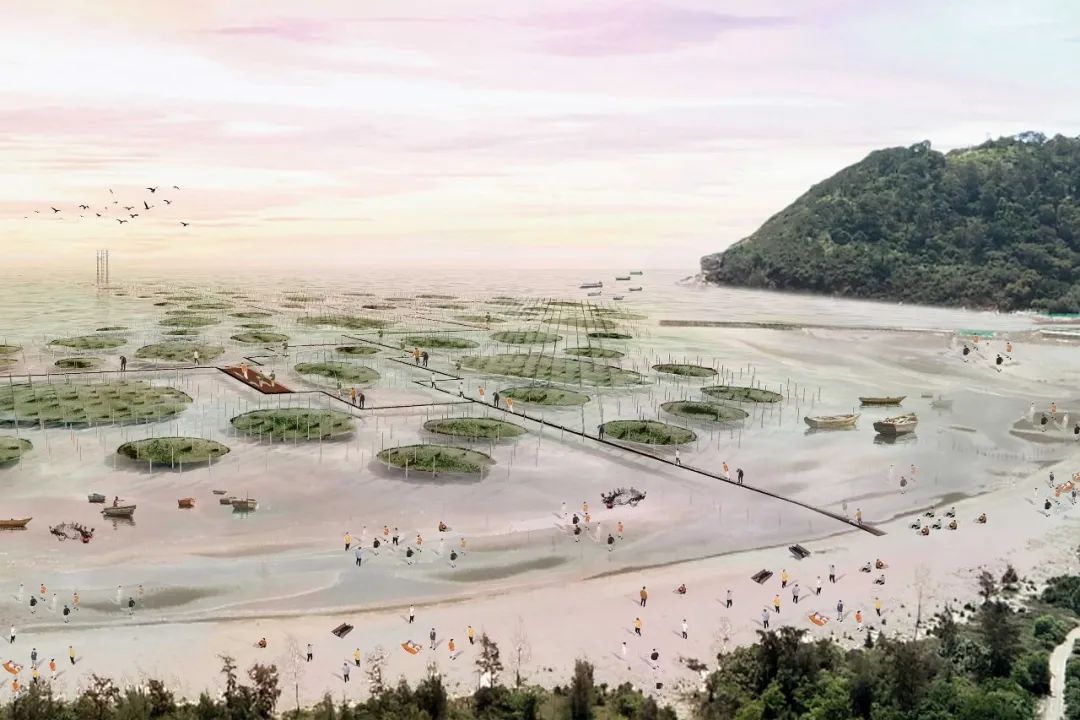
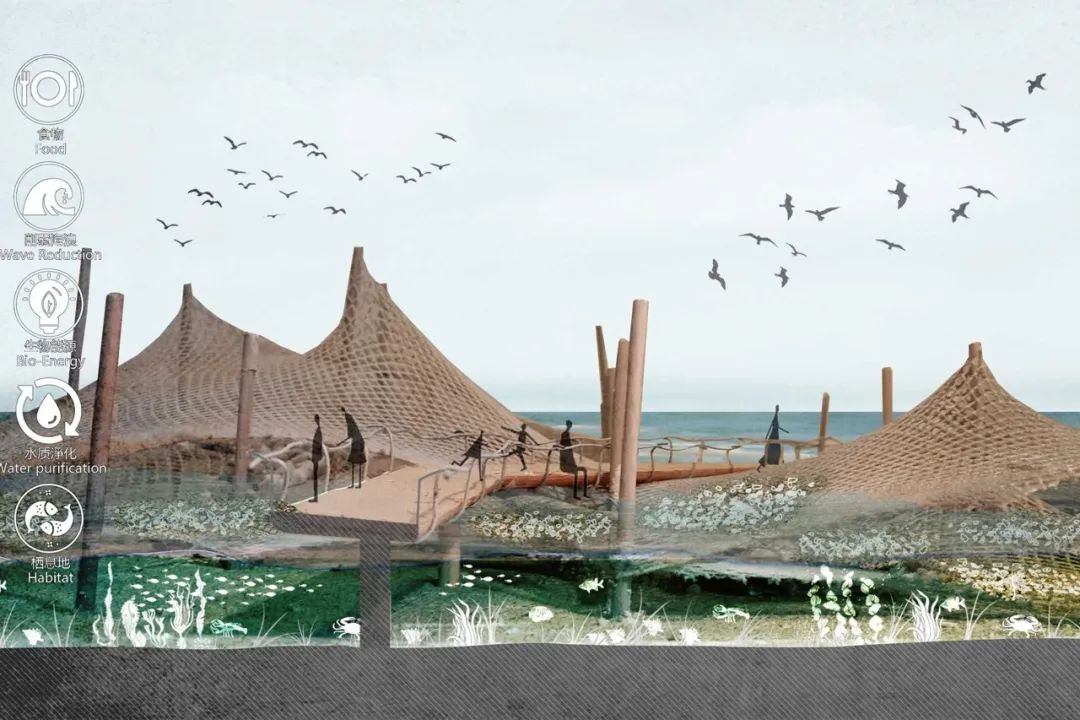
Thirdly, to further relieve sea flood pressure, Oyster Island occupies 130,000 m2 in the estuary and reduces peak flow velocity and waves while enriching estuary ecology.
Fourthly, local rainwater retention and controlled urban run-off is achieved by creating an urban blue-green network throughout the city. To improve the water quality of Chishi River, natural water purification measures are implemented in the tributary rivers.
Finally, Water management throughout the basin is optimized with a smart online system that integrates advanced modelling, water quality and quantity monitoring, and early flood warnings.
生物多样性 Abundant Ecology
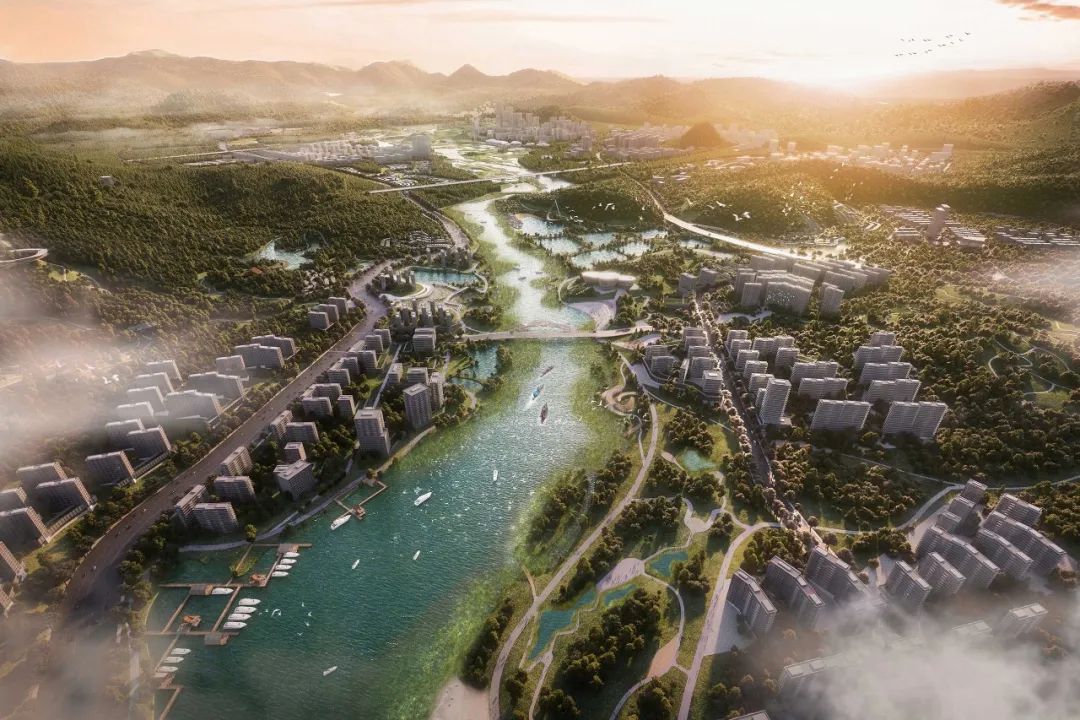



一、赤石河拥有极为宝贵的生境,如陆地森林淡水生境、微咸水生境和潮间带湿地。增强蓝绿色框架,增加容纳人类以及鱼类、鸟类、昆虫、植被及其栖息地的生态基础。
二、根据广泛的生态调查,15条野生动物走廊被战略性地放置在连接山、河、海和城市的地方。位于核心栖息地之间的另外 6 个生态垫脚石旨在提供不同栖息地的宝贵补丁,提供连通性并造福整个地区的生态。
三、生态价值最高的潮间带湿地连成河流为一体的区域潮汐公园,增加生物多样性和抗洪能力,将城市与自然联系起来,让居民体验拥有丰富栖息地的动态河流景观。
First, Chishi River has extremely valuable habitats, like terrestrial forest-freshwater habitats, brackish water habitats and intertidal wetlands.Chishi River’s enhanced blue-green framework is meanwhile the ecological foundation aimed at hosting humans as well as fish, birds, insects, vegetation, and their habitats.
Secondly, 15 wildlife corridors have been strategically placed connecting mountains, river, sea and city. A further 6 ecological steppingstones, positioned between core habitats, are intended to provide valuable patches of different habitats, providing connectivity and benefitting the ecology of the whole region.
Thirdly, The intertidal wetlands with the highest ecological value are connected to form a regional tidal park integrating rivers, increasing biodiversity and flood resistance, connecting the city with nature allowing residents to experience the dynamic river landscape with abundant habitats.
城乡和谐生活 Harmonious Urban-Rural Llving
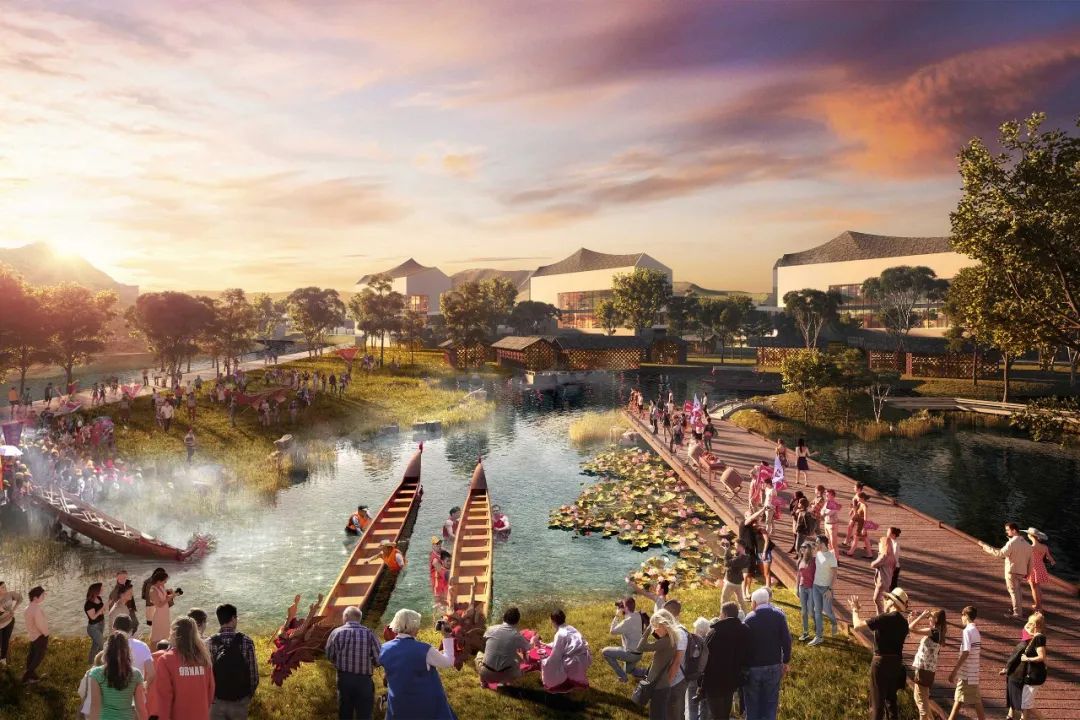
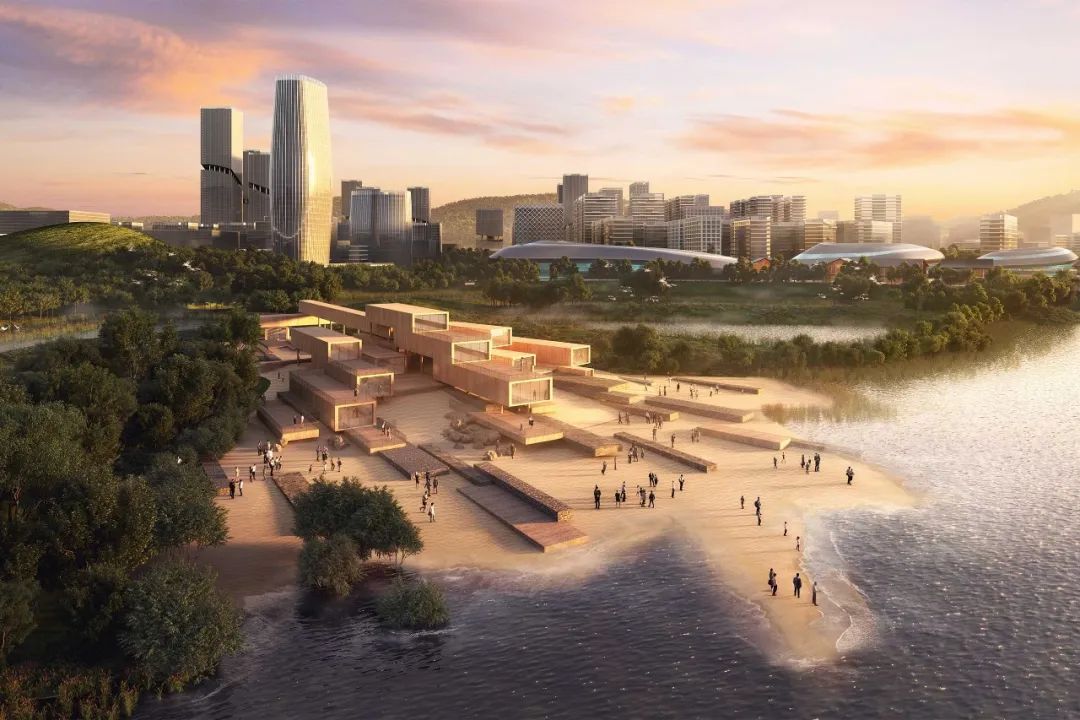
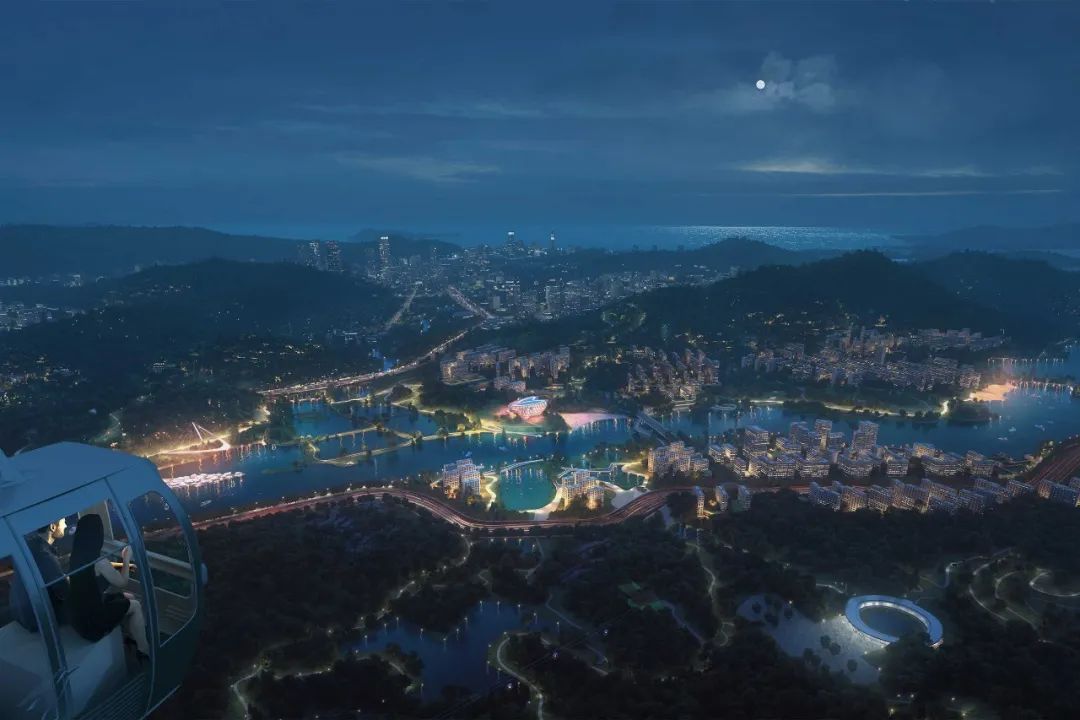



一、采用了各种策略保护和滋养文化遗产,一是尽可能完整地保留赤石古聚落景观:历史建筑、村落结构、相关山脉、农田、池塘、风水林。这些乡村景观成为城市内的“农业公园”,以其所环绕的村庄命名。作为他们的监护人和经营者,村民们维持着熟悉而有尊严的生计。
二、交通设计将城市设施、历史悠久的村庄和体验自然的地方平等地连接起来。以河流为中轴线,优化道路网络,城市聚落由绿指和河岸定义。一条 10 公里的大道(智能环路)连接老城区、交通枢纽、市中心和农业公园。这条大道将促进高科技与传统知识之间的创新和知识,同时将自然和文化带到深圳的家门口。
First,employs various strategies to preserve and nourish cultural heritage, First, the landscapes of Chishi’s ancient settlements are preserved as whole as possible: historical buildings, village structure, related mountains, farmlands, ponds, Fengshui forests. These rural landscapes become ‘Agricultural Parks’ within the city, named after the villages they encompass. As their guardians and operators, villagers maintain familiar and dignified livelihoods.
Secondly, transportation is designed to equally link urban amenities, historic villages, and places to experience nature. The river is used as a central axis to optimize the road network and urban settlements are defined by green fingers and riverbanks. A 10km avenue (Smart Loop) connects old town, traffic hub, city centre, and agricultural parks. This avenue will catalyse innovation and knowledge between high-tech and traditional knowledge, while bringing nature and culture to the doorstep of Shenzhen.
结语
Summarize
滨河50公里慢行道与公交节点无缝接驳。打造 “游乡、听河、登山、品城、尝海”五大主题游览路线,串联9景20个水岸目的地。上游竹筏乡野漂流,感受原乡风情,中游古老村镇里漫游,品尝山海的味道,或从凤河义渡古渡口乘坐游船,至下游河口观鸟感潮。通过赤石河上现代与传统结合的多元体验之路,体验最深圳的深汕,也是最汕尾的深汕。
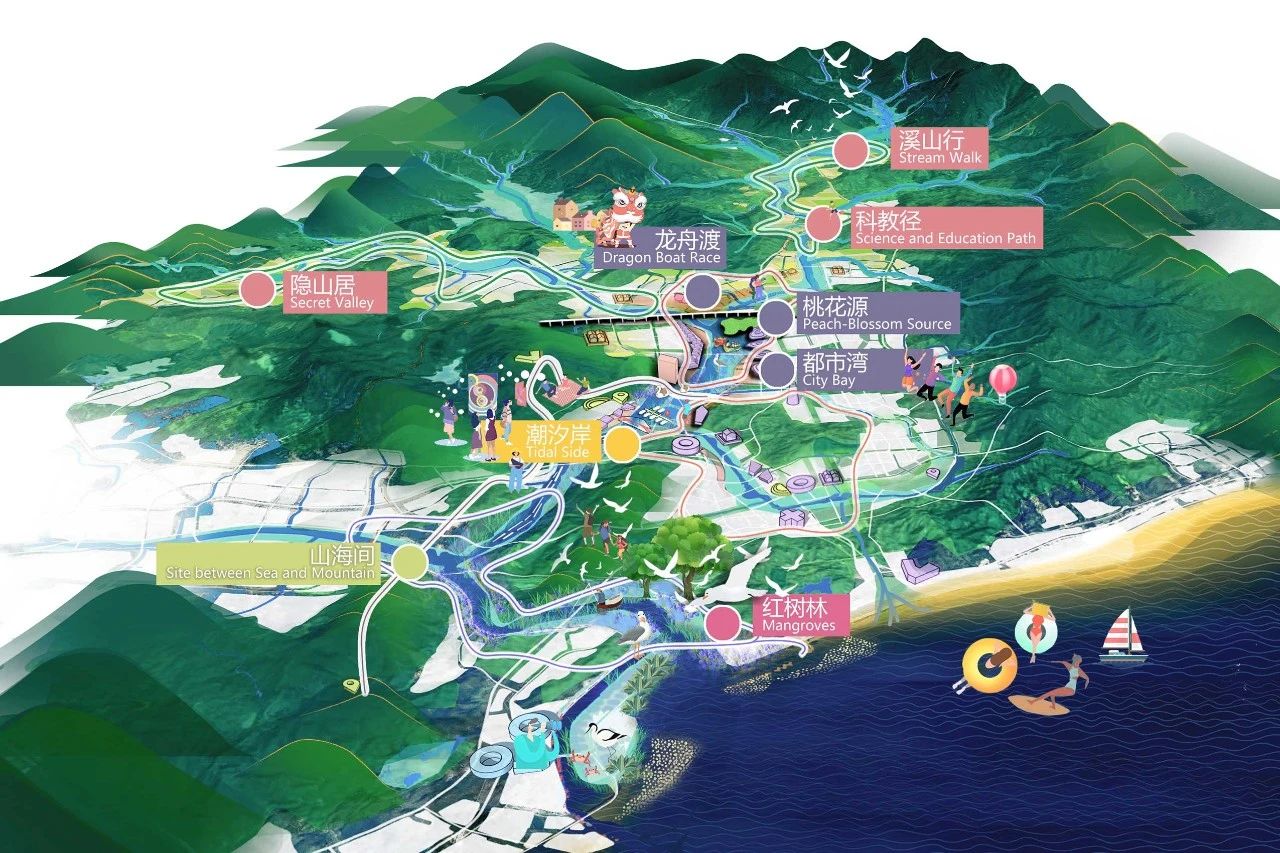
城市、乡村与山水耦合共生,“润泽之城”带来安全防灾、社会经济、基础设施、生态系统、和景观风貌的多元解决方案,塑造城市与自然双向平衡的未来先驱之城。
项目名称:深圳市深汕特别合作区赤石河一河两岸规划设计国际咨询
项目地点:深汕特别合作区
业主单位:深圳市规划和自然资源局、深圳市深汕特别合作区管理委员会
项目规模:约39.3平方公里
设计时间:2020年
设计特点:形成全流域韧性城市的发展格局;构建从山林源头、城市中心到潮汐通道的全周期水态示范区;塑造具有深汕味道、人文魅力的全要素山水景观带。
设计单位:
岭南设计集团有限公司(整体策划+景观专业)
中国电建集团华东勘测设计研究院(水利专业)
NL Urban Solutions B.V.(规划+生态专业)
纵横行咨询顾问有限公司(城市设计专业)
所获奖项:
国际咨询全球竞赛第一名
IFLA Asia-Pac LA Awards 荣誉奖
香港城市设计奖(规划/ 概念类) 大奖